| Total number of scaffolds | 413,763 |
|---|---|
| Total number of contigs | 648,787 |
| Total length of scaffolds (Mb) | 2723.8 |
| Total length of contigs (Mb) | 2449.7 |
| Percentage of gaps (%) | 10.1 |
| N/L50 of scaffolds | 648/1.1 Mb |
| N/L50 of contigs | 37,644/19.3 kb |
| Number of scaffolds longer than 50 kb | 4,297 |
| % main genome in scaffolds longer than 50 kb | 94.70% |
| X. laevis | X. tropicalis | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L chromosome | S chromosome | L + S chromosome | Chromosome | ||||||||
| Chr. | Length (Mb) | Gene Count | Chr. | Length (Mb) | Gene Count | Chr. | Length (Mb) | Gene Count | Chr. | Length (Mb) | Gene Count |
| Chr1L | 197 | 3,649 | Chr1S | 160 | 2,366 | Chr1L+S | 357 | 6,015 | Chr1 | 189 | 3,196 |
| Chr2L | 161 | 2,759 | Chr2S | 142 | 2,297 | Chr2L+S | 303 | 5,056 | Chr2 | 165 | 2,646 |
| Chr3L | 129 | 2,922 | Chr3S | 107 | 1,854 | Chr3L+S | 236 | 4,776 | Chr3 | 133 | 2,639 |
| Chr4L | 130 | 2,363 | Chr4S | 109 | 1,768 | Chr4L+S | 238 | 4,131 | Chr4 | 129 | 2,325 |
| Chr5L | 142 | 2,262 | Chr5S | 120 | 1,751 | Chr5L+S | 262 | 4,013 | Chr5 | 141 | 2,074 |
| Chr6L | 138 | 2,095 | Chr6S | 113 | 1,489 | Chr6L+S | 252 | 3,584 | Chr6 | 131 | 1,645 |
| Chr7L | 113 | 2,294 | Chr7S | 79 | 1,413 | Chr7L+S | 192 | 3,707 | Chr7 | 112 | 1,940 |
| Chr8L | 107 | 2,716 | Chr8S | 86 | 1,953 | Chr8L+S | 193 | 4,669 | Chr8 | 113 | 2,436 |
| Chr9_10L | 107 | 2,616 | Chr9_10S | 94 | 2,057 | Chr9_10L+S | 201 | 4,673 | Chr9 | 77 | 1,785 |
| Chr10 | 38 | 948 | |||||||||
| Total | 1,222 | 23,676 | Total | 1,010 | 16,948 | Total | 2,233 | 40,624 | Total | 1,227 | 21,634 |
| XenOrtho DB (Xenopus Ortholog DataBase) is a database in which ortholog genes of Xenopus tropicalis, Xenopus laevis and humans are listed. It was produced by Dr. Fukui (Faculty of Science and Engineering, Chuo Univ.) and Dr. Igawa (Hiroshima Univ. Amphibian Research Center) through collaboration between the Xenopus Community in Japan (XCIJ) and National Bio-Resource Project (NBRP). When a study using XenOrthoDB is published as a research paper, please acknowledge Dr. Fukui, Dr. Igawa, XCIJ, and NBRP. |

African clawed frog (right) and Western clawed frog (left)
Copyright: 2016 Shuji Takahashi @ Hiroshima University
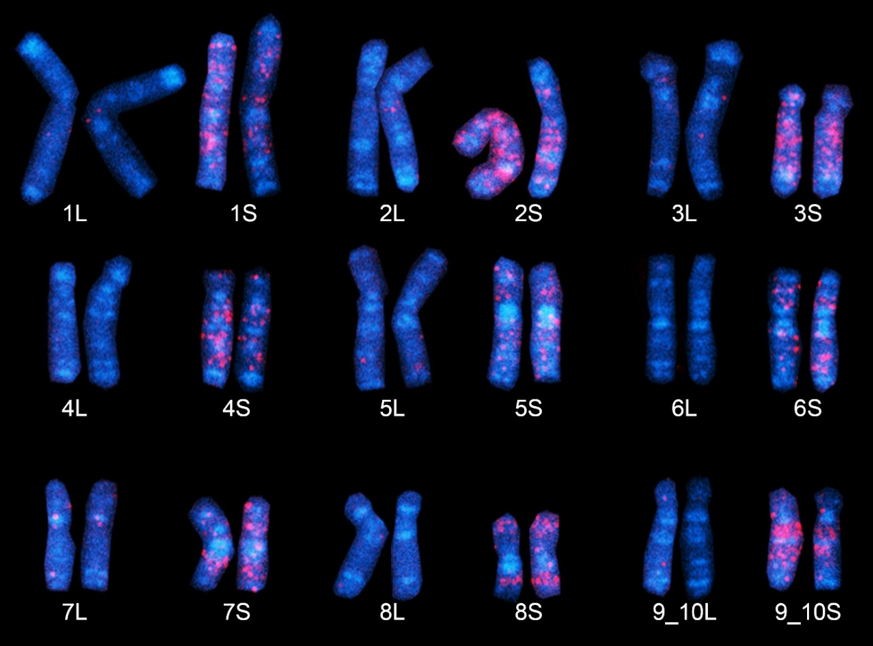
African clawed frog chromosomes
"Fossil" DNA sequences found only in the S subgenome (chromosomes) of Xenopus laevis emit a red glow employing the FISH method. The nine S chromosomes here clearly possess a larger number of red regions, believed to have derived from ancestral species S. (Chromosome 9, at bottom right, is represented as "9_10," as it corresponds to the fusion of ancestral chromosomes corresponding to chromosomes 9 and 10 in Xenopus tropicalis).Copyright: 2016 Yoshinobu Uno @ Nagoya University